Post 5: Install a logging solution for a Kubernetes homelab

Introduction - EfK stack on/for Kubernetes
Observability is a function that allows developers and operators to identify problems where and when they happen across multi-node systems. Proper instrumentation enables you to aggregate metrics, traces, logs and events from a distributed system and correlate them across various application components and services, identifying complex interactions between elements and allowing you to troubleshoot performance issues, improve management, and optimize cloud native infrastructure and applications.
This article covers running a logging solution hosted on, and supporting Kubernetes.
ELK is an acronym that describes a popular “stack” of open source components used to implement an n-tier logging solution with search, analytics and user interface. E=elasticsearch, L=Logstash, and K=Kibana. With Kubernetes it is often popular to swap out the L=Logstash component for f=fluentbit (aka EfK stack).
This substitution is popular because fluentbit is comparatively very light on resource demands (important because log collection elements run on every Kubernetes cluster node) and because it has a set of configurable input plugins that support gathering logs from Kubernetes itself plus the containers Kubernetes is hosting.
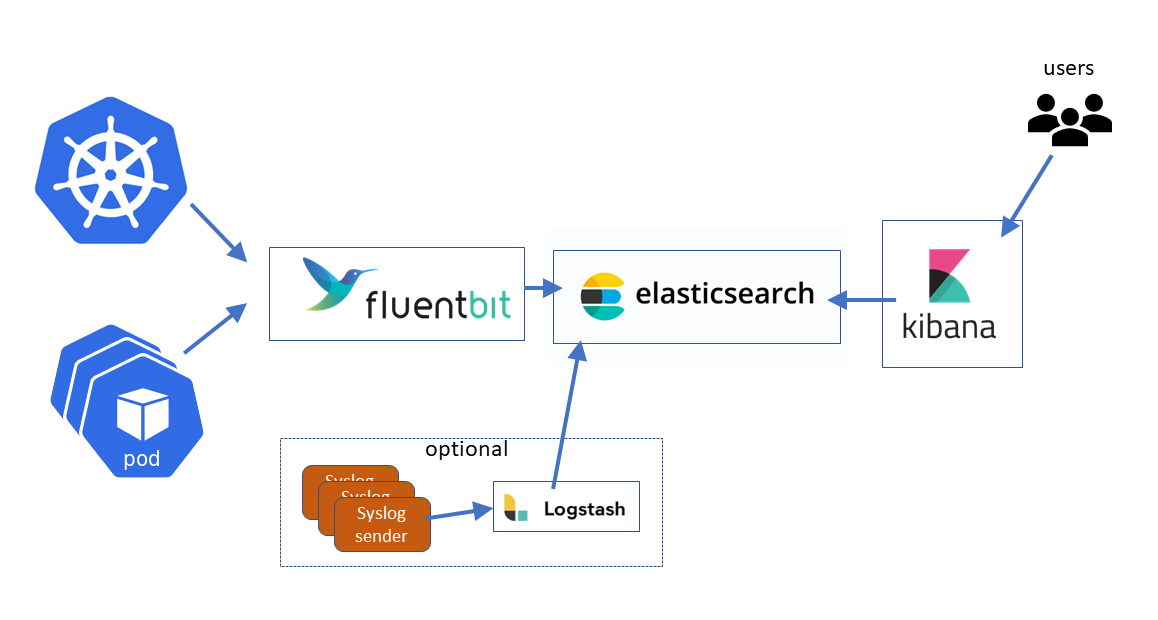
Install ElasticSearch and Kibana using a helm chart
The best practice is to use seven pods in the Elasticsearch cluster:
- Three master pods for managing the cluster.
- Two data pods for storing data and processing queries.
- Two client (or coordinating) pods for directing traffic. The “official” helm chart from elastic involves a multi-step process to do a horizontally scaled configuration like this so we are using the helm chart from bitnami instead.
Add the Bitnami helm repo if you don't already have it from a previous service installation:
helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami
helm repo updateThis example assumes you have a storage class pre-defined, named silver, and have a service load balancer in place. Adjust the steps as needed.
# create namespace
kubectl create ns kube-logging
# install
helm install elasticsearch bitnami/elasticsearch -n kube-logging --set global.storageClass=silver,global.kibanaEnabled=true,service.type=LoadBalancer,kibana.service.type=LoadBalancer,master.replicas=3,coordinating.service.type=LoadBalancerInstall Fluentbit using a Carvel package
To feed logs from Kubernetes to the Elasticsearch, Kibana combo - fluentbit will be used. This will cover an install using the Carvel based package option built into Tanzu Community Edition. If you are on a Kubernetes distribution that does not support Carvel, then a fluent bit install using helm with similar settings should work.
First a yaml file is composed to set inputs, outputs, parsers and filters appropriate for Kubernetes log collection.
cat << EOF > fluent-bit-data-values.yaml
namespace: "kube-logging"
fluent_bit:
config:
service: |
[Service]
Flush 1
Log_Level info
Daemon off
Parsers_File parsers.conf
HTTP_Server On
HTTP_Listen 0.0.0.0
HTTP_Port 2020
outputs: |
[OUTPUT]
Name es
Match *
Host elasticsearch
Port 9200
Logstash_Format On
Replace_Dots On
Retry_Limit False
Buffer_Size 64KB
Suppress_Type_Name On
inputs: |
[INPUT]
Name tail
Tag kube.*
Path /var/log/containers/*.log
Parser cri
DB /var/log/flb_kube.db
Mem_Buf_Limit 5MB
Skip_Long_Lines On
Refresh_Interval 10
[INPUT]
Name systemd
Tag kube_systemd.*
Path /var/log/journal
DB /var/log/flb_kube_systemd.db
Systemd_Filter _SYSTEMD_UNIT=kubelet.service
Systemd_Filter _SYSTEMD_UNIT=containerd.service
Read_From_Tail On
Strip_Underscores On
filters: |
[FILTER]
Name kubernetes
Match kube.*
Kube_URL https://kubernetes.default.svc:443
Kube_CA_File /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt
Kube_Token_File /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token
Kube_Tag_Prefix kube.var.log.containers.
Merge_Log On
Merge_Log_Key log_processed
K8S-Logging.Parser On
K8S-Logging.Exclude On
parsers: |
# see https://github.com/fluent/fluent-bit/blob/v1.7.5/conf/parsers.conf
[PARSER]
Name apache
Format regex
Regex ^(?<host>[^ ]*) [^ ]* (?<user>[^ ]*) \[(?<time>[^\]]*)\] "(?<method>\S+)(?: +(?<path>[^\"]*?)(?: +\S*)?)?" (?<code>[^ ]*) (?<size>[^ ]*)(?: "(?<referer>[^\"]*)" "(?<agent>[^\"]*)")?$
Time_Key time
Time_Format %d/%b/%Y:%H:%M:%S %z
[PARSER]
Name apache2
Format regex
Regex ^(?<host>[^ ]*) [^ ]* (?<user>[^ ]*) \[(?<time>[^\]]*)\] "(?<method>\S+)(?: +(?<path>[^ ]*) +\S*)?" (?<code>[^ ]*) (?<size>[^ ]*)(?: "(?<referer>[^\"]*)" "(?<agent>[^\"]*)")?$
Time_Key time
Time_Format %d/%b/%Y:%H:%M:%S %z
[PARSER]
Name apache_error
Format regex
Regex ^\[[^ ]* (?<time>[^\]]*)\] \[(?<level>[^\]]*)\](?: \[pid (?<pid>[^\]]*)\])?( \[client (?<client>[^\]]*)\])? (?<message>.*)$
[PARSER]
Name nginx
Format regex
Regex ^(?<remote>[^ ]*) (?<host>[^ ]*) (?<user>[^ ]*) \[(?<time>[^\]]*)\] "(?<method>\S+)(?: +(?<path>[^\"]*?)(?: +\S*)?)?" (?<code>[^ ]*) (?<size>[^ ]*)(?: "(?<referer>[^\"]*)" "(?<agent>[^\"]*)")?$
Time_Key time
Time_Format %d/%b/%Y:%H:%M:%S %z
[PARSER]
Name json
Format json
Time_Key time
Time_Format %d/%b/%Y:%H:%M:%S %z
[PARSER]
Name docker
Format json
Time_Key time
Time_Format %Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S.%L
Time_Keep On
[PARSER]
Name docker-daemon
Format regex
Regex time="(?<time>[^ ]*)" level=(?<level>[^ ]*) msg="(?<msg>[^ ].*)"
Time_Key time
Time_Format %Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S.%L
Time_Keep On
[PARSER]
# http://rubular.com/r/tjUt3Awgg4
Name cri
Format regex
Regex ^(?<time>[^ ]+) (?<stream>stdout|stderr) (?<logtag>[^ ]*) (?<message>.*)$
Time_Key time
Time_Format %Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S.%L%z
[PARSER]
Name logfmt
Format logfmt
[PARSER]
Name syslog-rfc5424
Format regex
Regex ^\<(?<pri>[0-9]{1,5})\>1 (?<time>[^ ]+) (?<host>[^ ]+) (?<ident>[^ ]+) (?<pid>[-0-9]+) (?<msgid>[^ ]+) (?<extradata>(\[(.*)\]|-)) (?<message>.+)$
Time_Key time
Time_Format %Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S.%L
Time_Keep On
[PARSER]
Name syslog-rfc3164-local
Format regex
Regex ^\<(?<pri>[0-9]+)\>(?<time>[^ ]* {1,2}[^ ]* [^ ]*) (?<ident>[a-zA-Z0-9_\/\.\-]*)(?:\[(?<pid>[0-9]+)\])?(?:[^\:]*\:)? *(?<message>.*)$
Time_Key time
Time_Format %b %d %H:%M:%S
Time_Keep On
[PARSER]
Name syslog-rfc3164
Format regex
Regex /^\<(?<pri>[0-9]+)\>(?<time>[^ ]* {1,2}[^ ]* [^ ]*) (?<host>[^ ]*) (?<ident>[a-zA-Z0-9_\/\.\-]*)(?:\[(?<pid>[0-9]+)\])?(?:[^\:]*\:)? *(?<message>.*)$/
Time_Key time
Time_Format %b %d %H:%M:%S
Time_Format %Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S.%L
Time_Keep On
[PARSER]
Name kube-custom
Format regex
Regex (?<tag>[^.]+)?\.?(?<pod_name>[a-z0-9](?:[-a-z0-9]*[a-z0-9])?(?:\.[a-z0-9]([-a-z0-9]*[a-z0-9])?)*)_(?<namespace_name>[^_]+)_(?<container_name>.+)-(?<docker_id>[a-z0-9]{64})\.log$
streams: ""
plugins: ""
daemonset:
resources: { }
podAnnotations: { }
podLabels: { }
EOFtanzu package install fluent-bit --package-name fluent-bit.community.tanzu.vmware.com --version 1.7.5 --namespace kube-logging --values-file fluent-bit-data-values.yamlExamine logs using the Kibana UI
Wait for all pods in the kube-logging namespace to start.
- Use
kubectl get svc -n kube-loggingto get the external load balanced ip of the kibana ui. - Open
http://<kibana ip>:5601in a browser - Dismiss the integration popup, click on the menu on the left, then discover
- Create a data view
- Set index pattern to logstash-* Note that the trailing asterisk will be added automatically
- Choose @timestamp from dropdown.
- Choose discover and select “last 15 minutes”. You should see log entries. Refer to the ElasticSearch/Kibana online docs or videos for more details on how this can be used
